|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sapera Machine Vision Software: Astrocyte Artificial Intelligence gets smarter
Back
to Newsletter
Go to Software
Go to Astrocyte product
page
Go
to Sapera Processing product page
|
Sapera
Vision Software 2022-05 for machine vision applications
|
|
Sapera Software is designed for a broad range of applications, from precision metrology to pharmaceutical packaging. With an easy to use interface, Sapera provides a suite of tools that can be readily applied to a multitude of automated inspection tasks, such as positioning, measuring, identification and flaw detection.
|
|
What
is new in Edition 2022-05 of Sapera Vision Software?
|
|
Astrocyte
1.30
|
|
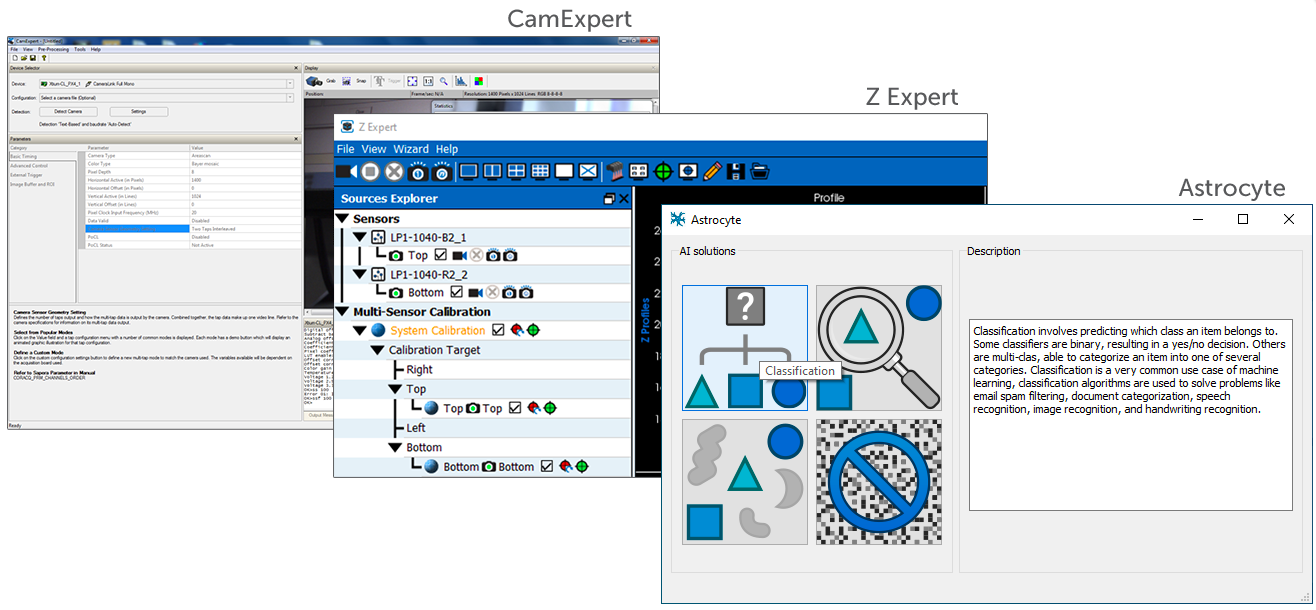
Astrocyte
is a code-free AI training tool to quickly deploy AI models for
machine vision tasks. It allows users to use their own images
of products, samples, and defects to train neural networks to
perform applications like anomaly detection, classification, object
detection, segmentation, and noise reduction.
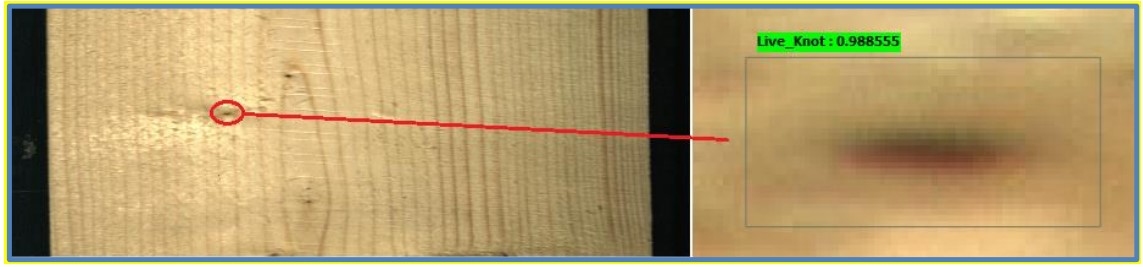
In the example above, tiling is used to identify knots on wooden planks. The input image has a resolution of 2800 x 1024 and contains knots with sizes as low as 10 pixels.
Increased
Performance on Anomaly Detection
|
|
Sapera
Processing 9.30.
|
|
Sapera Processing is the key component to the overall Sapera Vision Software platform. Sapera Processing is an extensive library of image processing, image analysis and AI functions dedicated to application development, integration, and deployment. In version 9.30 of Sapera Processing new functions and improvements are introduced mostly on the AI and 3D tools. |
Need
a price or more application information? Please
email Adept Turnkey or call our offices |
|
If you like this page, please recommend and share it. |
|||
| More | |||





 Astrocyte
1.30 offers YOLOX, an additional object detection algorithm. It
is more compact and offers improved performance capabilities than
the existing SSD (Single Shot Detector) algorithm. Because of
its compactness, YOLOX is widely used in embedded devices.
Astrocyte
1.30 offers YOLOX, an additional object detection algorithm. It
is more compact and offers improved performance capabilities than
the existing SSD (Single Shot Detector) algorithm. Because of
its compactness, YOLOX is widely used in embedded devices.